Which Type of Intellectual Property Protection Do I Need?
Art Law Journal
JUNE 30, 2022
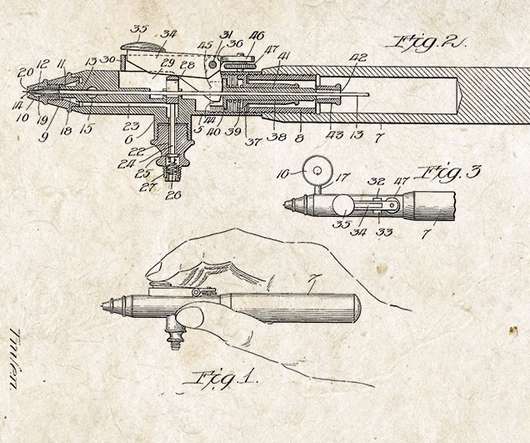
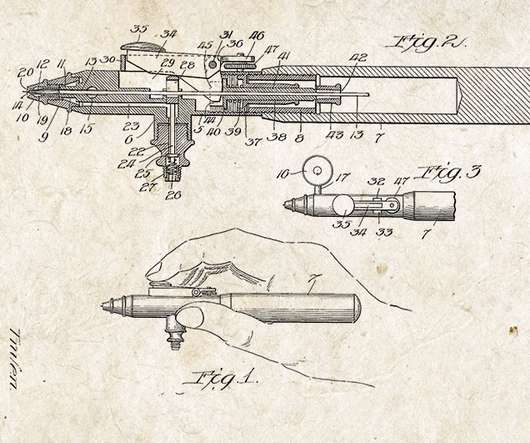
Unfortunately, Intellectual Property law has gotten so complicated that many people aren’t even sure which type of Intellectual Property (copyright, trademarks, or patents) protects their creative work. Which Type of Intellectual Property Law Is Right for You. Your Copy-Rights.






Let's personalize your content