Evergreening of Patents
Kashishipr
OCTOBER 20, 2021
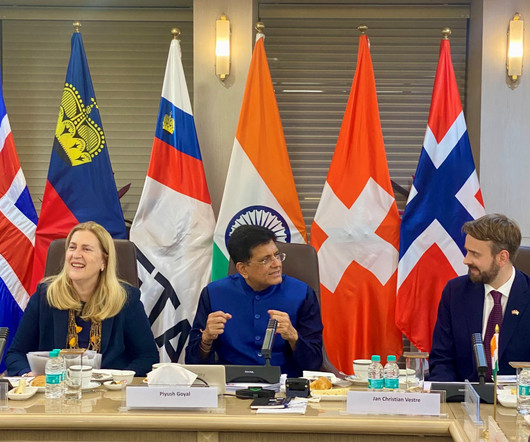
The main objective of Sections 26C and 27D was to prevent the patent holders from getting an extension on their patents by taking advantage of loopholes and undue benefits of the Justice system. India changed its Patents Laws in 2005 to comply with the TRIPS Agreement. Conclusion. For more visit: [link].





Let's personalize your content